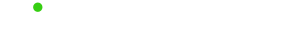Lithium is the first member of the alkali metal family. The alkali metals are the elements that makeup Group 1 (IA) of the periodic table. The periodic table is a chart that shows how chemical elements are related to one another. The alkali metals include sodium, potassium, rubidium, cesium, and rancium. Lithium is also the least dense of all metals. It has a density of about half that of water. Lithium has several important and interesting uses. In recent years, it has been used to make lightweight, efficient batteries.
Lithium-based cells are named for their active materials; the words are either written in full or shortened by their chemical symbols. A series of letters and numbers strung together can be hard to remember and even harder to pronounce, and battery chemistries are also identified in abbreviated letters.
For example, lithium cobalt oxide, one of the most common Li-ions, has the chemical symbols LiCoO2 and the abbreviation LCO. For reasons of simplicity, the short form Li-cobalt can also be used for this battery. Cobalt is the main active material that gives this battery character. Other Li-ion chemistries are given similar short-form names. This section lists six of the most common Li-ions.